Causes of Diabetes Complications
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood glucose levels. Over time, uncontrolled diabetes can lead to a wide range of complications affecting multiple organ systems. Understanding the causes of these complications is critical for managing diabetes effectively and preventing long-term health issues.
One of the primary causes of diabetes complications is prolonged exposure to high blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia). When blood sugar levels remain elevated for extended periods, they can damage blood vessels and nerves throughout the body. This damage results in complications such as diabetic retinopathy (vision problems), neuropathy (nerve damage), and nephropathy (kidney disease).
In addition to hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, particularly in type 2 diabetes, plays a significant role in the development of complications. Insulin resistance occurs when the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin, which leads to elevated glucose levels in the blood. This metabolic dysfunction contributes to chronic inflammation and oxidative stress, further damaging tissues and increasing the risk of cardiovascular complications, such as heart disease and stroke.
Another factor influencing diabetes complications is genetic predisposition. Certain genetic variants can affect how the body metabolizes glucose and responds to hormonal signals that regulate blood sugar. These genetic factors can make some individuals more susceptible to specific complications, such as diabetic retinopathy or peripheral artery disease. By understanding these genetic influences, healthcare providers can better tailor treatment plans to reduce the risk of complications.
Explore more on how genetics influence diabetes – Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Types of Diabetes Complications
Diabetes can lead to a wide variety of complications, affecting several systems in the body. These complications fall into several categories, including cardiovascular issues, nerve damage, and microvascular complications.
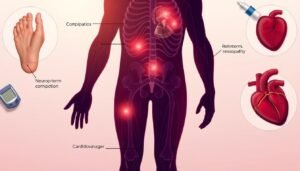
1. Cardiovascular Complications
People with diabetes are at an increased risk for cardiovascular diseases, including coronary artery disease, heart attack, stroke, and peripheral vascular disease. The underlying cause of these complications is often atherosclerosis, where plaque builds up in the blood vessels, reducing blood flow and increasing the risk of clot formation. Uncontrolled blood sugar levels can accelerate the progression of atherosclerosis, making it more likely that individuals with diabetes will experience heart disease or stroke.
2. Neuropathy (Nerve Damage)
Diabetic neuropathy refers to nerve damage that results from prolonged high blood sugar levels. Symptoms can include tingling, numbness, burning pain, and weakness in the affected areas, often starting in the hands or feet. Neuropathy can also affect the autonomic nervous system, leading to problems with digestion, heart rate, and even sexual function. In severe cases, nerve damage can be irreversible and significantly impact an individual’s quality of life.
3. Microvascular Complications
Diabetic retinopathy and diabetic nephropathy are two major microvascular complications caused by high blood sugar levels.
- Diabetic Retinopathy: This condition affects the small blood vessels in the retina and is a leading cause of vision loss among adults with diabetes. Damage to these blood vessels can lead to blurred vision, dark spots, and, in severe cases, blindness.
- Diabetic Nephropathy: High blood glucose levels can also damage the blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to kidney dysfunction and even kidney failure if not properly managed.
Both diabetic retinopathy and nephropathy require regular monitoring and management to prevent further complications.
Learn more about diabetic complications – National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
Monitoring and Preventing Diabetes Complications
For individuals living with diabetes, monitoring and preventing complications are crucial to maintaining overall health.
Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels
Regular blood glucose monitoring is essential to ensure that blood sugar levels remain within target ranges. This can be done at home using a glucometer or through lab tests ordered by a healthcare provider. Keeping blood sugar levels under control is the first step in preventing the complications associated with diabetes.
Regular Medical Check-ups
In addition to monitoring blood glucose, individuals with diabetes should undergo regular medical check-ups. These check-ups may include:
- Eye exams to detect diabetic retinopathy.
- Kidney function tests to monitor for signs of diabetic nephropathy.
- Foot exams to check for signs of neuropathy or potential foot ulcers.
Early detection of complications is essential to prevent further progression and improve treatment outcomes.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing complications involves a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, medication adherence, and regular medical check-ups. Some key strategies include:
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help control blood sugar levels and reduce fluctuations that may lead to complications.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, promotes cardiovascular health, and aids in weight management, which is particularly important for individuals with type 2 diabetes.
- Medication: Taking prescribed medications as directed by a healthcare provider is essential for maintaining blood glucose control and reducing the risk of complications.
Check out the ADA’s guidelines on managing diabetes – American Diabetes Association.
More Information
Diabetes is a complex condition, and staying informed is key to managing it effectively. Reliable resources include:
- The American Diabetes Association (ADA), which provides information on the latest research, treatment options, and lifestyle recommendations.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) offer comprehensive guides on prevention, management, and complications of diabetes.
For personalized guidance, it is crucial to consult with healthcare professionals specializing in endocrinology or diabetology, who can provide tailored advice and treatment plans.
Conclusion
Understanding the complications of diabetes mellitus is essential for both individuals living with the condition and healthcare providers. By recognizing the causes and types of complications, we can better manage and prevent them. Regular monitoring, early intervention, and a proactive approach to lifestyle changes are key to reducing the risk of severe complications. With support from healthcare providers and ongoing education, individuals with diabetes can take control of their health and live fulfilling lives.

